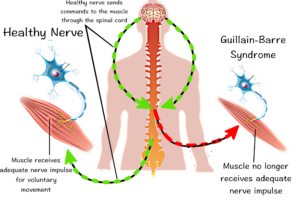
Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune attack on the nervous system that affects 3,000 to 6,000 people per year. This devastating attack causes muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis. Symptoms resolve within weeks to months, however, some will experience permanent nerve damage. Rehabilitation is critical to prevent damage to joints and muscles while muscles recover back to full strength. Here are several essential GBS facts everyone should know to prevent secondary injury and promote a timely recovery.
Is pain normal with Guillain Barre Syndrome?
Guillain Barre Syndrome can cause problems with every part of the nervous system. Here are the most common problems that may occur.
- Tingling in your fingers, toes, hands and feet
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty with bladder and bowel function
- Rapid Heartrate
- Severe pain
- Leg weakness
- Arm weakness (less common)
- Neurologic Fatigue
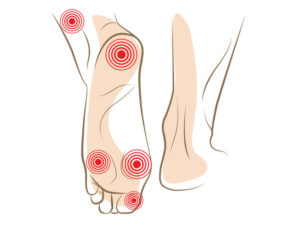
Why do my feet hurt all the time?
Fact #1 Damage to Sensory Nerves Causes Hypersensitivity
GBS damages sensory nerves that carry messages to the brain. This group of nerves is responsible for light touch, hot and cold, pressure, pin prick, and pain. As these nerves recover, they may become overactive which may intensify these sensations. Additionally, damage to these nerves may cause unusual sensations such as numbness, tingling, and burning.
Physical Therapy will focus on desensitization strategies to treat over active sensations. Abnormal sensations will decrease over time as the nerve recovers and regains normal function.
Why do I always feel tired?
Fact #2 Muscle Fatigue Can Delay Recovery
Damage also occurs to nerves that supply the electrical input to muscles (motor nerves). Motor nerves are the power source that allows muscles to contract. So, why does this matter? With less input, the muscle can’t handle the same load as a healthy muscles. Therefore, muscles are at risk for early muscle fatigue and muscle failure. Muscle failure causes a cascade of chemical events within the muscle that cause tissue damage and will delay recovery.
How do you prevent muscle failure?
Avoid resistance (for example using dumb bells and resistance bands). Increase repetitions progressively. Muscle soreness should NOT last more than 24 hours after exercising. If muscles do not recover within 24 hours decrease the number of repetitions.
Do I have to wear a brace if I am recovering from Guillain Barre Syndrome?
Fact #3 Weak Muscles Cause Secondary Damage to Joints and Muscles
Muscle weakness in the leg can cause an abnormal walking pattern and lead to secondary injuries. For instance, when there is weakness in the quadriceps and hamstrings (muscles around the knee), the knee will hyperextend and cause damage to the back of the knee. Weakness in the hip muscles can result in a variety of postural problems causing hip and back pain.
How do you prevent secondary injury?
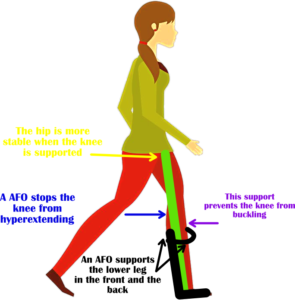
Bracing may be necessary to prevent further joint damage while the muscle regains strength. An ankle foot orthosis (AFO) is a brace that supports the ankle. Despite the name, this is NOT only a ” foot and ankle support”. An AFO is really a leg support. Why? Not only does an AFO lift the foot (when stepping), and stabilize the ankle (in standing). It also keeps the lower leg upright preventing the knee from buckling (falling forward) and hyperextending (bending backward). Finally, an AFO can also provide stability to the hip. When the leg has this support, the hip does not have to work as hard to keep the body upright.
Now, I know what some of you may be thinking. Doesn’t this prevent the muscles from getting stronger? With other conditions, this is a valid concern. For example, with a nerve compression injury or a muscle injury, the goal is to stimulate the nerve and strengthen the muscle. With these other conditions, you may want to be cautious with bracing as it may impede recovery. However, GBS is different. Muscle recovery with GBS requires time. Time for the antigens (bad substance attacking the nerves) to clear out of the system. Therefore, the goal is to protect the body while this process is occurring.
Why does my walking look different?
Fact #4 Weak Muscles Cause Compensations
When muscles are weak, you may resort to compensatory strategies (using stronger muscles to substitute for weaker muscles). If the hip muscles are not strong enough to lift the leg, you may be prone to compensate with lower back muscles when walking (steppage gait). If the ankle muscles that lift the foot are weak (drop foot) you may compensate by using hip and back muscles to lift the leg higher so that you do not catch your foot on the ground.
Steppage Gait
These compensations can result in lower back and hip pain.
How do you prevent injury due to compensations?
A physical therapist will perform a careful movement analysis to identify the weak muscles that may be causing compensations. It is critical to avoid compensations. Once these compensations are identified, a therapist will teach you how to move while the weaker muscle regain strength.
Why does EVERYTHING make me tired?
Fact #5 Guillain Barre Syndrome can cause Central Fatigue
Fatigue is defined as a strong feeling of tiredness and a decrease in the ability to maintain mental and physical performance. Central (brain) fatigue is a decreased ability to think, solve problems, retain information, and maintain attention. Peripheral fatigue is the muscle’s inability to perform voluntary movement. Unfortunately, Guillain Barre Syndrome can result in peripheral fatigue AND central fatigue (indirectly). Everything is requiring more time and energy. It is also common to feel discouraged and/or depressed following such a life changing event. It is important to schedule plenty of rest breaks throughout the day. Rest breaks will give your mind and your body a chance to recharge and give you the energy you need to get through the day.
Learn More About GBS






I had guillian barre syndrome 4 1/2 years ago. My feet still hurt, burn and tingle almost nonstop. I am 67 years old. Is this just something I am going to have to deal with? Thank you for your time.